Topic Modeling
Original Source: https://www.coursera.org/specializations/data-science-python
Semantic Text Similarity
1. Path Similarity
PathSim(a, b) = 1/(1+(length of shortest path between a & b))
Before you calculate similarity between texts, you need to specify the word’s meaning by doing as follows.
import numpy as np
import nltk
# nltk.download() # only at first time
from nltk.corpus import wordnet as wn
import pandas as pd
deer = wn.synset('deer.n.01')
elk = wn.synset('elk.n.01')
horse = wn.synset('horse.n.01')
print('deer: '+ deer.definition())
print('elk: ' + elk.definition())
print('horse: ' + horse.definition())
deer: distinguished from Bovidae by the male's having solid deciduous antlers
elk: large northern deer with enormous flattened antlers in the male; called `elk' in Europe and `moose' in North America
horse: solid-hoofed herbivorous quadruped domesticated since prehistoric times
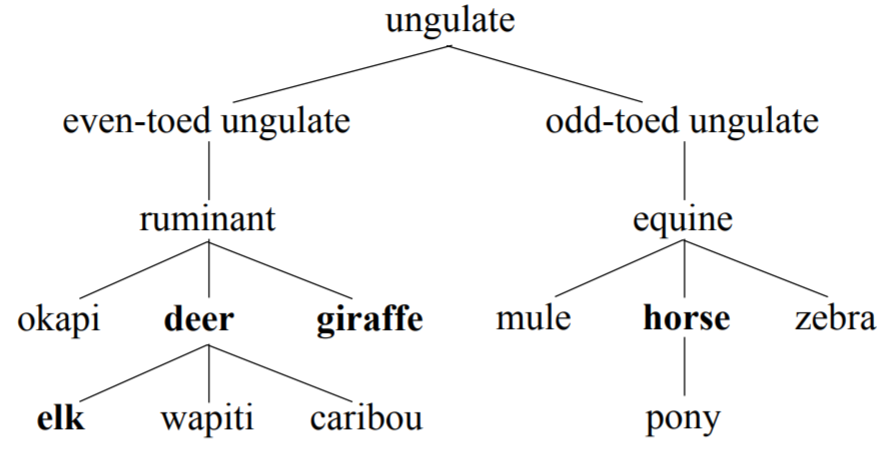
print(deer.path_similarity(elk))
print(deer.path_similarity(horse))
0.5
0.14285714285714285
2. Lin Similarity
Least Common Subsumer (LCS): Closest ancestor to both concepts
LinSim(u, v) = 2logP(LCS(u,v)) / (logP(u)+logP(v)) *P(LCS(u,v)) represents the amount of information contained in the LCS of the two concepts
To calculate Lin Similarity, you need to load an information content file from the wordnet_ic corpus.
from nltk.corpus import wordnet_ic
brown_ic = wordnet_ic.ic('ic-brown.dat')
print(deer.lin_similarity(elk, brown_ic))
print(deer.lin_similarity(horse, brown_ic))
0.8623778273893673
0.7726998936065773
3. Distributional Similarity
“Two words that frequently appears in similar contexts are more likely to be semantically related”
Pointwise Mutual Information(PMI) is one measurement of distributional similarity.
PMI(w,c) = log (P(w,c) / P(w)P(c))
doc = nltk.corpus.gutenberg.words('austen-emma.txt')
print(len(doc))
doc[:10]
192427
['[', 'Emma', 'by', 'Jane', 'Austen', '1816', ']', 'VOLUME', 'I', 'CHAPTER']
Find 10 pair of words that are most similar according to distributional similarity found in doc
from nltk.collocations import *
bigram_measures = nltk.collocations.BigramAssocMeasures()
finder = BigramCollocationFinder.from_words(doc)
finder.nbest(bigram_measures.pmi, 10)
[('----', 'mum'),
('.]', 'WINDSOR'),
('1816', ']'),
('26th', 'ult'),
('Abominable', 'scoundrel'),
('Agricultural', 'Reports'),
('Austen', '1816'),
('Clayton', 'Park'),
('DEAR', 'MADAM'),
('Farmer', 'Mitchell')]
Excercise - Document Similarity
We will compute path similarity between two documents. To do that, we will construct following functions.
convert_tag:converts the tag given bynltk.pos_tagto a tag used bywordnet.synsets.doc_to_synsets:returns a list of synsets in document. This function should first tokenize and part of speech tag the document usingnltk.word_tokenizeandnltk.pos_tag. Then it should find each tokens corresponding synset usingwn.synsets(token, wordnet_tag). The first synset match should be used. If there is no match, that token is skipped.similarity_score:returns the normalized similarity score of a list of synsets (s1) onto a second list of synsets (s2). For each synset in s1, find the synset in s2 with the largest similarity value. Sum all of the largest similarity values together and normalize this value by dividing it by the number of largest similarity values found. Missing values should be ignored.document_path_similarity:computes the symmetrical path similarity between two documents by finding the synsets in each document usingdoc_to_synsets, then computing similarities usingsimilarity_score.
doc1 = 'This is a function to test document_path_similarity.'
doc2 = 'Use this function to see if your code in doc_to_synsets \
and similarity_score is correct!'
def convert_tag(tag):
tag_dict = {'N': 'n', 'J': 'a', 'R': 'r', 'V': 'v'}
try:
return tag_dict[tag[0]]
except KeyError:
return None
tokens_tags = nltk.pos_tag(nltk.word_tokenize(doc1))
print(tokens_tags)
print([convert_tag(tag[1]) for tag in tokens_tags])
[('This', 'DT'), ('is', 'VBZ'), ('a', 'DT'), ('function', 'NN'), ('to', 'TO'), ('test', 'VB'), ('document_path_similarity', 'NN'), ('.', '.')]
[None, 'v', None, 'n', None, 'v', 'n', None]
def doc_to_synsets(doc):
tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(doc)
tokens_tags = nltk.pos_tag(tokens)
converted_tags = [convert_tag(tag[1]) for tag in tokens_tags]
synsets = [wn.synsets(token, converted_tag) for (token, converted_tag) in zip(tokens, converted_tags)]
valid_synsets = [synset[0] for synset in synsets if len(synset) != 0]
return valid_synsets
print(doc1)
print(doc_to_synsets(doc1))
This is a function to test document_path_similarity.
[Synset('be.v.01'), Synset('angstrom.n.01'), Synset('function.n.01'), Synset('test.v.01')]
def similarity_score(s1, s2):
sim1 = []
for synset1 in s1:
sim2 = []
for synset2 in s2:
similarity = wn.path_similarity(synset1, synset2)
if similarity is not None:
sim2.append(similarity)
if sim2:
sim1.append(max(sim2))
return sum(sim1)/len(sim1)
print(similarity_score(doc_to_synsets(doc1), doc_to_synsets(doc2)))
print(similarity_score(doc_to_synsets(doc2), doc_to_synsets(doc1)))
0.6125
0.49603174603174605
def document_path_similarity(doc1, doc2):
synsets1 = doc_to_synsets(doc1)
synsets2 = doc_to_synsets(doc2)
return (similarity_score(synsets1, synsets2) + similarity_score(synsets2, synsets1)) / 2
document_path_similarity(doc1, doc2)
0.554265873015873
Now, we will use function document_path_similarity to find out if a document is paraphrase of another.
paraphrases = pd.read_csv('paraphrases.csv')
paraphrases.head()
| Quality | D1 | D2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | Ms Stewart, the chief executive, was not expec... | Ms Stewart, 61, its chief executive officer an... |
| 1 | 1 | After more than two years' detention under the... | After more than two years in detention by the ... |
| 2 | 1 | "It still remains to be seen whether the reven... | "It remains to be seen whether the revenue rec... |
| 3 | 0 | And it's going to be a wild ride," said Allan ... | Now the rest is just mechanical," said Allan H... |
| 4 | 1 | The cards are issued by Mexico's consulates to... | The card is issued by Mexico's consulates to i... |
- Find the pair of documents in paraphrases which has the maximum similarity score.
def most_similar_docs():
similarity = np.array([document_path_similarity(d1, d2) for (d1, d2) in zip(paraphrases['D1'], paraphrases['D2'])])
max_index = similarity.argmax()
return paraphrases.loc[max_index, 'D1'], paraphrases.loc[max_index, 'D2'], similarity[max_index]
most_similar_docs()
('"Indeed, Iran should be put on notice that efforts to try to remake Iraq in their image will be aggressively put down," he said.',
'"Iran should be on notice that attempts to remake Iraq in Iran\'s image will be aggressively put down," he said.\n',
0.9753086419753086)
- Provide labels for the twenty pairs of documents by computing the similarity for each pair using
document_path_similarity. Let the classifier rule be that if the score is greater than 0.75, label is paraphrase (1), else label is not paraphrase (0). Report accuracy of the classifier using scikit-learn’s accuracy_score.
def label_accuracy():
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# Your Code Here
similarity = np.array([document_path_similarity(d1, d2) for (d1, d2) in zip(paraphrases['D1'], paraphrases['D2'])])
predictions = (similarity>0.75).astype(int)
return accuracy_score(paraphrases['Quality'], predictions)
label_accuracy()
0.8
Topic Modeling
Topic Modeling is a process to find topics which are represented as a word distribution from a document.
We know distribution of the number of words per topic by analyzing large corpus. Also, we know distribution of the number of words found in a given document. With these, it is possible to predict which topics the document will deal with.
1. PLSA (Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis)
2. LDA (Latent Dirichlet Allocation)
Excercise - Using LDA to find topics from a document
import pickle
import gensim
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
# Load the list of documents
with open('newsgroups', 'rb') as f:
newsgroup_data = pickle.load(f)
newsgroup_data[0][:100]
"The best group to keep you informed is the Crohn's and Colitis Foundation\nof America. I do not know"
First, train ldamodel from ‘newsgroups’. Number of topics is 10.
Use argument id2word to map id of the word to word
# Use CountVectorizor to find three letter tokens, remove stop_words,
# remove tokens that don't appear in at least 20 documents,
# remove tokens that appear in more than 20% of the documents
vect = CountVectorizer(min_df=20, max_df=0.2, stop_words='english',
token_pattern='(?u)\\b\\w\\w\\w+\\b')
# Fit and transform
X = vect.fit_transform(newsgroup_data)
# Convert sparse matrix to gensim corpus.
corpus = gensim.matutils.Sparse2Corpus(X, documents_columns=False)
# Mapping from word IDs to words (To be used in LdaModel's id2word parameter)
id_map = dict((v, k) for k, v in vect.vocabulary_.items())
# Use the gensim.models.ldamodel.LdaModel constructor to estimate LDA model parameters on the corpus, and save to the variable `ldamodel`
ldamodel = gensim.models.ldamodel.LdaModel(corpus, id2word=id_map, num_topics=10, passes=25, random_state=0)
Using ldamodel, find a list of the 10 topics and the most significant 10 words in each topic.
ldamodel.show_topics()
[(0,
'0.059*"car" + 0.019*"cars" + 0.018*"000" + 0.013*"100" + 0.012*"high" + 0.011*"speed" + 0.011*"oil" + 0.011*"driving" + 0.010*"auto" + 0.010*"200"'),
(1,
'0.025*"time" + 0.018*"just" + 0.017*"bike" + 0.014*"don" + 0.014*"good" + 0.011*"know" + 0.010*"used" + 0.009*"use" + 0.009*"want" + 0.009*"turn"'),
(2,
'0.019*"just" + 0.019*"don" + 0.014*"new" + 0.013*"good" + 0.012*"know" + 0.011*"think" + 0.010*"years" + 0.009*"little" + 0.009*"people" + 0.009*"really"'),
(3,
'0.026*"don" + 0.020*"think" + 0.020*"does" + 0.016*"say" + 0.015*"people" + 0.014*"know" + 0.013*"just" + 0.013*"did" + 0.011*"believe" + 0.011*"argument"'),
(4,
'0.015*"way" + 0.014*"pain" + 0.014*"edu" + 0.014*"good" + 0.013*"things" + 0.013*"pick" + 0.012*"pitt" + 0.012*"soon" + 0.011*"gordon" + 0.011*"low"'),
(5,
'0.023*"people" + 0.021*"god" + 0.016*"ground" + 0.013*"science" + 0.011*"religion" + 0.011*"current" + 0.011*"point" + 0.010*"theory" + 0.009*"example" + 0.009*"evidence"'),
(6,
'0.029*"drive" + 0.020*"disk" + 0.017*"card" + 0.016*"use" + 0.015*"scsi" + 0.015*"does" + 0.014*"drives" + 0.014*"hard" + 0.014*"thanks" + 0.013*"controller"'),
(7,
'0.087*"edu" + 0.068*"com" + 0.025*"new" + 0.022*"period" + 0.019*"john" + 0.016*"second" + 0.015*"leafs" + 0.014*"runs" + 0.014*"power" + 0.013*"rangers"'),
(8,
'0.036*"game" + 0.032*"team" + 0.027*"year" + 0.021*"games" + 0.015*"season" + 0.015*"players" + 0.015*"good" + 0.015*"play" + 0.014*"hockey" + 0.013*"win"'),
(9,
'0.045*"space" + 0.024*"data" + 0.023*"nasa" + 0.019*"information" + 0.017*"available" + 0.014*"center" + 0.013*"program" + 0.012*"ftp" + 0.012*"edu" + 0.011*"use"')]
For the new document new_doc, find the topic distribution.
new_doc = ["\n\nIt's my understanding that the freezing will start to occur because \
of the\ngrowing distance of Pluto and Charon from the Sun, due to it's\nelliptical orbit. \
It is not due to shadowing effects. \n\n\nPluto can shadow Charon, and vice-versa.\n\nGeorge \
Krumins\n-- "]
new_doc_vect = vect.transform(new_doc)
new_corpus = gensim.matutils.Sparse2Corpus(new_doc_vect, documents_columns=False)
list(ldamodel.get_document_topics(new_corpus))[0]
[(0, 0.020000454),
(1, 0.020002134),
(2, 0.02000191),
(3, 0.020002013),
(4, 0.020001262),
(5, 0.020001087),
(6, 0.020000191),
(7, 0.57224584),
(8, 0.020001762),
(9, 0.26774335)]
Information Extraction
1. Named Entity Recognition
Named entities: Noun phrases that are of specific type and refer to specific person, organization, location,…
Approaches to identify named entities: Regular expressions, machine learning,…
2. Relation Extraction
Identify relationships between named entities
Example : In Erbitux helps treat lung cancer, extracts the relation that erbitux is the treatment of lung cancer.
3. Co-reference Resolution
Disambiguate mentions and group mentions together
Example : In Anita met Joseph at the market. He surprised her with a rose., finds out that her referse to Anita and He refers to Joseph
4. Question Answering
Builds on named entity recognition, relation extraction, and co-reference resolution.
Given a question, finds the most appropriate answer from the text.
Example : What does Erbitux Treat?



Leave a Comment